Finally, digitally-transformed, patient-centered care
Vigor provides consumer-led, home-based chronic disease and rehabilitation care which is remotely monitored via connected devices and supported by AI and multi-disciplinary care teams.
Without Vigor:
Disparate in-person appointments at specialist facilities
With Vigor:
Evidence-based collaborative care delivered to your home
Seamless consumer experience
Vigor sets our members up for success across all physical, virtual, and interpersonal touch points.
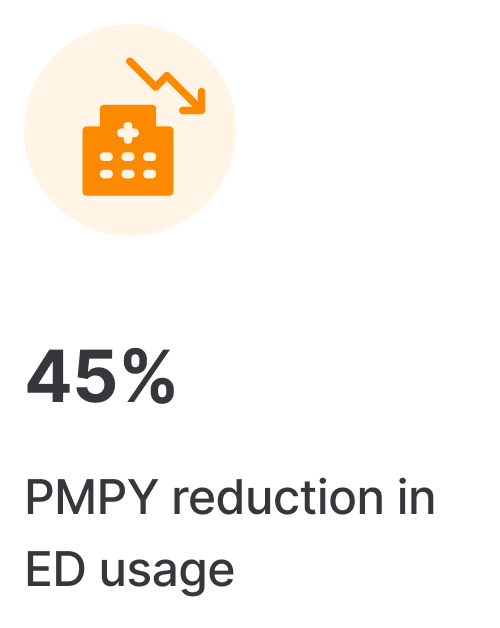
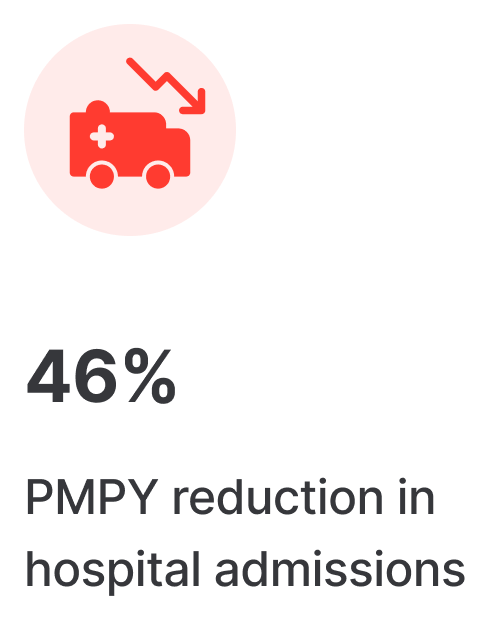
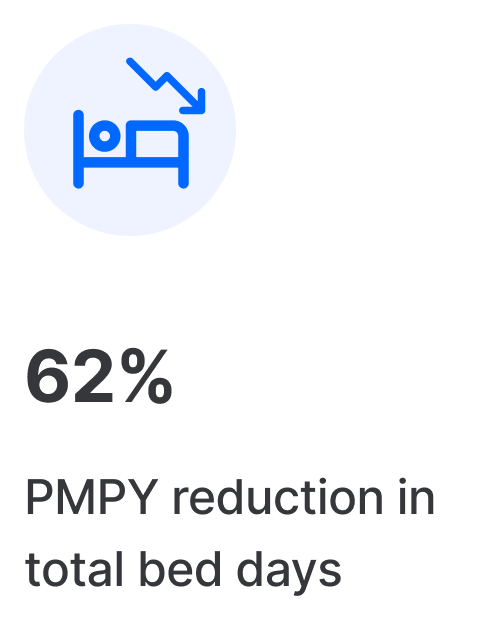
Results you’ve been looking for
Vigor scales clinically-proven programs to increase access, improve quality, and lower the total cost of chronic disease and rehabilitation care.
-
Spitzer, Kerry A et al. “Participation in Pulmonary Rehabilitation after Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease among Medicare Beneficiaries.” Annals of the American Thoracic Society vol. 16,1 (2019): 99-106. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201805-332OC
Katajisto, Milla, and Tarja Laitinen. “Estimating the effectiveness of pulmonary rehabilitation for COPD exacerbations: reduction of hospital inpatient days during the following year.” International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease vol. 12 2763-2769. 22 Sep. 2017, doi:10.2147/COPD.S144571
Cecins, Nola et al. “Reduction in hospitalisation following pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with COPD.” Australian health review : a publication of the Australian Hospital Association vol. 32,3 (2008): 415-22. doi:10.1071/ah080415
Dalal, Anand A et al. “Costs of COPD exacerbations in the emergency department and inpatient setting.” Respiratory medicine vol. 105,3 (2011): 454-60. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2010.09.003
All-in-one care coordination platform
The Vigor Command Center™ is a breakthrough care collaboration platform for clinicians and care teams, enabling intelligent care for thousands of patients at scale.
What industry leaders say about Vigor
“Vigor is much more than remote patient monitoring, they provide counseling, education, exercise, nutrition, medication management – comprehensive pulmonary rehabilitation services - we need this! Pulmonary rehabilitation is proven to improve outcomes and we don’t have enough pulmonary rehabilitation capacity.”
“Vigor’s home-based chronic disease management program has achieved amazing outcomes with our initial member cohort. We need to offer Vigor to every eligible plan member.”
“We are updating our medical policies to enable us to pay for Vigor’s evidence-based programs.”